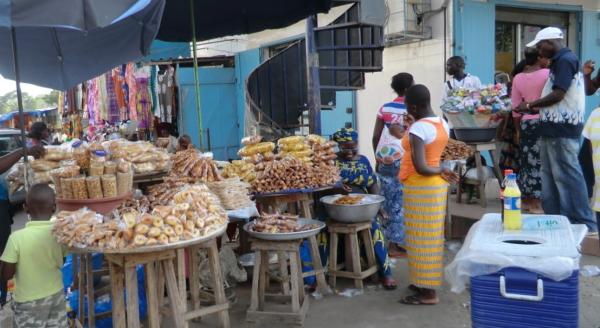Call to action 24 August 2023
- Home
- Our activities, our impact
- Tropical value chains
- Sorghum
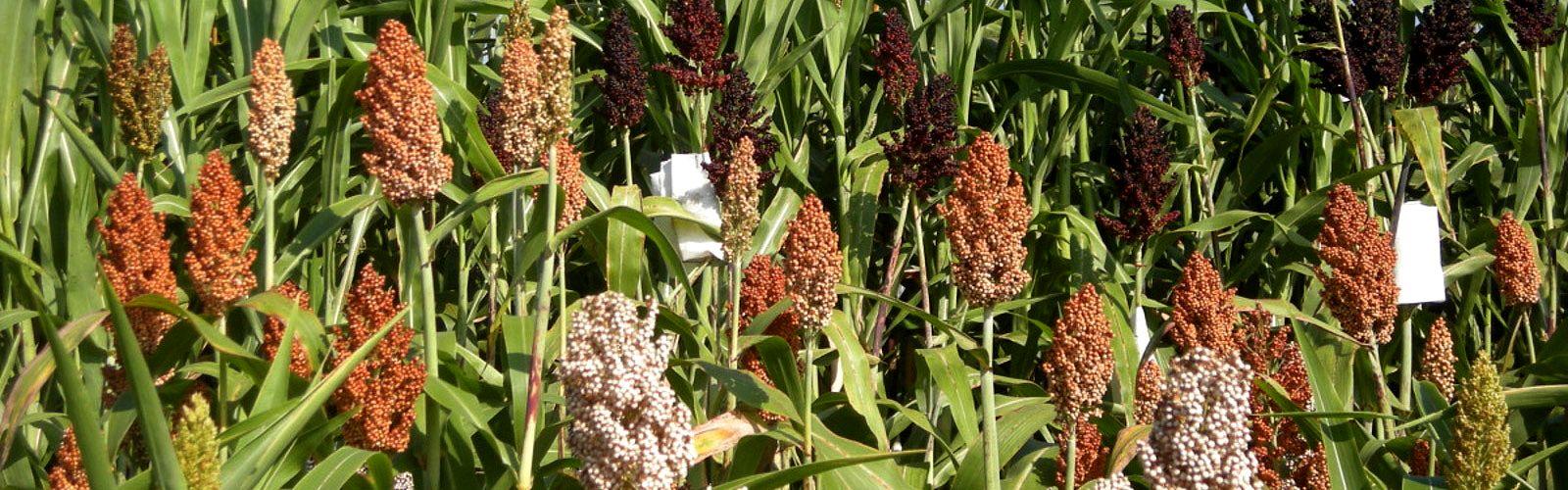

Sorghum
The figures for sorghum
- 5th cereal grown worldwide (in terms of grain production and area planted).
- 60 Mt per year.
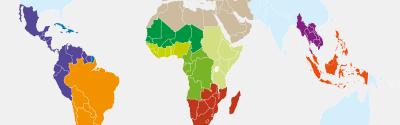
- In terms of area planted, the three leading producing countries are Sudan (6,9 M° ha), Nigeria (5,7), India (4,2)
- In terms of output, the US is well ahead of the pack (11 million tonnes in 2021), followed by Nigeria (6,7), India (5,3), Ethiopia (4,4) Mexico (4,3).
- It is a staple in the diet of 300 million people in semi-arid tropical zones.
A plant with multiple potential uses
- Grain to feed people and animals
- High food-value forage in various forms (green, hay or silage)
- Soluble sugars can be extracted from sweet sorghum varieties to make syrups, ethanol, 1st-generation fuel ethanol or alcohol/spirits
- Lignocellulosic biomass to generate energy via methanization, thermal plants and 2nd-generation fuel ethanol production, and to make composite plastics or building blocks
- Cover crop to conserve soils and remobilize minerals within DMC systems
- Various high-added-value molecules for agro-industry: tannins, anthocyanins (pigments), kafirins, aconitic acid, etc.
The issues
For semi-arid tropical regions
- Making sorghum substantially more competitive (boosting yield potential and tailoring grain quality to market demand) in areas where cereal crop intensification is under way.
- Making production more consistent by maintaining good grain quality (in sanitary, technological and nutritional terms) in zones with strong climatic constraints, where sorghum is primarily a subsistence crop.
- Diversifying food use of grain sorghum in Africa to boost producer incomes and create jobs in rural areas.
- Developing food and non-food use of multi-purpose sweet sorghums.
- Making better use of sorghum's potential to contribute to agroecological intensification as a pest and disease regulator and/or cover crop.
For France and Europe
- Developing varieties and crop management sequences for temperate supply chains and building stakeholder networks for biomass sorghum (animal feed, energy, construction).
- Making better use of sorghum's potential to provide ecosystem services (polluted soil detoxification or stabilization, etc.).